How Does Blockchain Work?
In the vast world of technology, few innovations have garnered as much attention as blockchain. You might have heard about it in the context of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but the truth is, that blockchain is a versatile technology with applications reaching far beyond digital currencies. So, without any further ado, let’s break into the article to learn more about this revolutionary technology.
What is Blockchain?
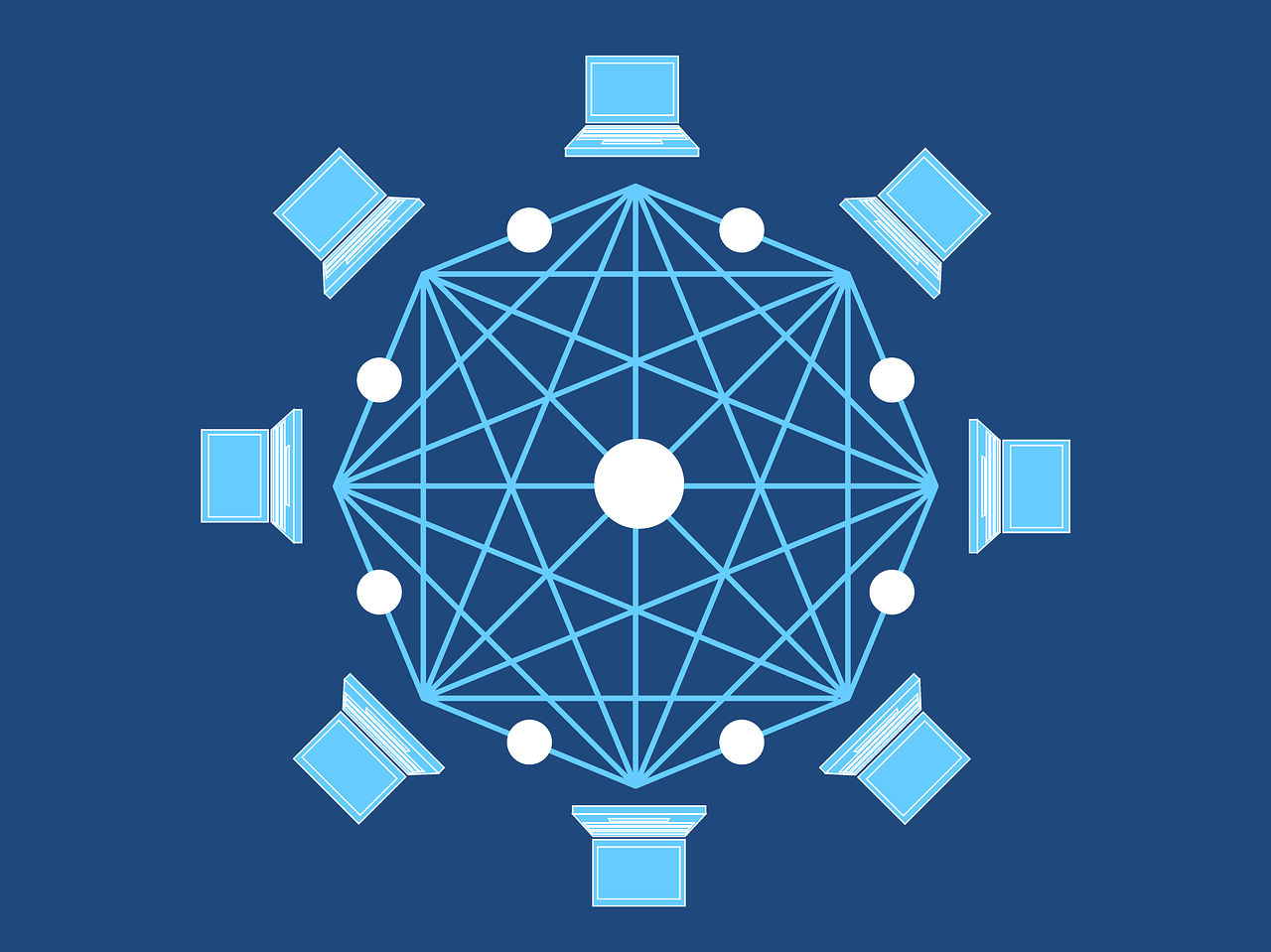
At its core, blockchain is like a super-secure digital ledger. It records and verifies transactions across a decentralized network of computers without any tampering. Originally introduced with Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved, finding its way into various industries due to its key features like decentralization, transparency, and security.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Although blockchain technology comes in various forms, including Public Blockchain, Private Blockchain, Hybrid Blockchain, and Consortium Blockchain, their operational foundations share common principles. Hence, the guide below will provide you an overview of how blockchain works. So, keep scrolling the article.
1. Transaction Input:
When someone initiates a transaction, it means they’re either sending or receiving something valuable, like digital money. However, this action must go through a verification process to ensure it’s legitimate. Think of it like having to show your ID before making a purchase.
2. Block Creation:
Valid transactions are grouped into what we call a “block.” This block is like a container that holds a bunch of these transactions. It simplifies things and helps keep track of them in a structured manner, making it easier for the system to manage. Additionally, to ensure security, each block is linked to the previous one using a unique identifier called a “hash,” creating a chain of blocks, which makes it extremely challenging for anyone to tamper with the information.
3. Network Distribution:
Once the block is created, it doesn’t stay in one place. It gets sent to every computer in the network. Imagine making photocopies of a document and giving one to each person in a meeting. This ensures that everyone has the same information.
4. Validation by Nodes:
Special computers in the network, often called “nodes” or “miners,” have an important job. They check the transactions in the block to make sure everything is correct and follows the rules. If everything checks out, they add this block to the existing chain of blocks, creating what we call a “blockchain.” As a reward for their efforts, these nodes receive cryptocurrency, providing them with an incentive to keep the network running smoothly.
5. Network Update:
The updated blockchain, now including the new block with the recent transactions, is shared with everyone in the network. It’s like distributing the meeting minutes after a discussion so that everyone is on the same page. Now, all the computers have the most up-to-date information about who sent what to whom.
Security Measures:
The security of the blockchain comes from two main things. First, each block is linked to the previous one using something called a “hash.” It’s like putting a unique seal on each box, making it extremely difficult for someone to open it without permission. Second, all the computers in the network must agree on the new transactions. This teamwork ensures that if someone tries to mess with the transactions, the network pauses until the issue is sorted out, preventing any one computer from causing trouble. This combination of cryptographic security and network consensus makes the blockchain a reliable and tamper-resistant system
Few BlockChain Examples And Cases
Blockchain, more than just for money, helps in many areas. In the supply chain, it helps track products from start to finish, stopping fake things from sneaking in and making deliveries smoother. In healthcare, it keeps your medical information safe and lets you decide who sees it. For IDs, it’s like having a digital ID card you can carry around, making things safer and simpler.
In voting, it ensures fair elections by being super secure and transparent, and you can even vote from far away. In money matters, blockchain makes transactions faster, and big players like PayPal use it for buying and selling cryptocurrencies. Lastly, in fun stuff like concerts, blockchain lets artists earn more by tracking ticket resales transparently. A good example is TixTo.Me by Live Nation SAS.
Conclusion
In short, blockchain helps products move better, keeps your health info safe, makes IDs simpler, ensures fair votes, speeds up money stuff, and even makes concerts better for artists. It’s like a super trustworthy digital helper across lots of things
.